Cutting-edge Molecular Diagnostics for Early Disease Detection

Notable Achievements
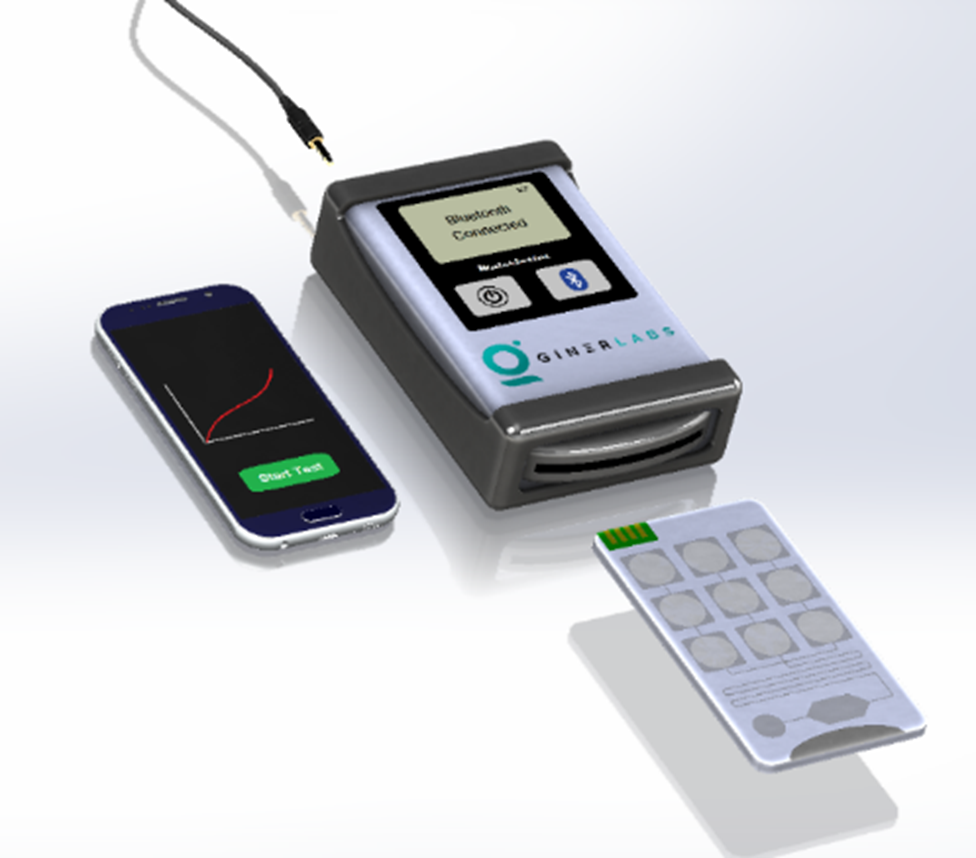
Giner, Inc. consistently engages in a wide range of projects, including the development of aptamers and nucleic acid-based electrochemical and other biosensors. Among our notable achievements is the aptamer-based multiplexed detection of opioid metabolites in wastewater samples, boasting a detection limit of 27 pg/mL. This groundbreaking work was co-published in ACS Nano (2022) and highlighted in Science Daily, Boston College. Additionally, our team at Giner has made significant progress in detecting multiple gene biomarkers (CYP2D6 and CYP2C19 and their allele variants) associated with drug metabolism and in non-invasively detecting oxytocin peptide at 1 pg/mL in saliva (published in International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2023), blood, and hair extract samples. Our research also extends to the development of fungal gene sensors, achieving an impressive limit of detection equivalent to 10 copies/mL for Histoplasma genes, including CBP1, M-antigen, and HCP100, as published in Biosensors and Bioelectronics in 2023.
Furthermore, we have advanced the non-invasive detection of cancer gene mutations and personalized therapy for non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Giner’s PCR-enhanced ligation assay delivers genomic DNA sensitivity down to 2 copies/µL, corresponding to mutation allele frequency (MAF) levels of 0.01%. This fulfills the clinical sensitivity requirement and surpasses the sensitivity of the current standard digital droplet PCR (ddPCR) by 10-fold, which has a limit of 0.1% for MAF. Ongoing work aims to adapt the assay for multiplexed ctDNA detection, validate with patient plasma samples, and integrate into a prototype, thus achieving a significant milestone toward regulatory evaluation. Fully developed, this technology will facilitate the enactment of personalized therapy, improve treatment outcomes, and offer significant advantages over existing methods such as lower test cost, easier sample preparation, and faster sample-to-result turnaround.
Publications
- I. Riley#, T. Regan#, M. Rana, P. Xie, A.A. Argun, “Development and Validation of an HPLC-MS/MS Method for the Quantitative Detection of Opioid Metabolites in Wastewater” (#co-first authors), Submission is in progress.
- M. Rana, P. Xie, A. Aasi, A.A. Argun, “Detection of Oral Drugs in NIX-TB Regimen for Therapeutic Monitoring of Multidrug Resistant Tuberculosis” Submission is in progress.
- M. Rana, M. Stewart, M. Rodrigues, E. Toprak, A. Koh, A.A. Argun, “An Ultrasensitive and Novel Gene Sensor to Monitor Gut Microbiome” Submission is in progress.
- Z. Azam, X. Zhang, R. Wahab, M.M. Hasan, S. Dhadhal, B. Kang, MM Hassan, M. Karim, J.U. Choi, M. Rana, J-Y. Zhang, S. Roy, Y. Byun, I-S. Kim, J.Y. Song, E.P. Toy, S.Y. Reddy, F. Alam, T.A. Al-Hilal, “Doppel as an early-stage biomarker promoting EMT and dissemination in ovarian cancers” International Journal of Cancer (2025); 1-14, DOI: 10.1002/ijc.70268
- R. Wahab, A. Keshavarz, Z. Azam, T. Islam, MM Hasan, X. Zhang, A. Alobaida, M. Rana, J.U. Choi, F. Alam, I-S Kim, Y. Byun, J.H. McCarty, N. P. Nickel, S. Roy, T.A Al-Hilal, “Microfluidic captured patient-derived circulating endothelial cells identify novel targets of pulmonary arterial hypertension” Biomaterials (2025), Volume 323, 123429.
- M. Rana#, A. Weber#, M. Stewart, A.A. Argun, “Rapid and Low-Cost Field Toxin Analysis to Monitor Harmful Algal Blooms” (#co-first authors), Biosensors and Nanotheranostics (2025), 4 (1) 1-10
- M. Stewart, D. Donaldson, A.A. Argun, M Rana, “ Smartphone-Integrated Point-of-Care Sensor for Rapid and Sensitive Malaria Detection in Resource-Limited Settings” Biosensors and Nanotheranostics (2025), 4 (1) 1-7
- M. Rana, S.M. Asil, C. Boutin, M.J. Kachwala, J. Espejo, A.A. Argun, “ Detection of EGFR Mutations T790M and L858R for Therapeutic Guidance of NSCLC” Journal of Thoracic Oncology (2024), Volume 19, Issue 10, S496
- Z. Azam, X. Zhang, R. Wahab, M.M. Hasan, B. Kang, MM Hassan, M. Karim, J.U. Choi, M. Rana, J-Y. Zhang, S. Roy, Y. Byun, I-S. Kim, J.Y. Song, F. Alam, E.P. Toy, S.Y. Reddy, T.A. Al-Hilal, “The prion-like protein Doppel: A soluble biomarker steering ovarian cancer’s peritoneal to circulatory dissemination” bioRxiv preprint (2024), doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/2024.07.26.605386
- M. Rana, N. Yildirim, N. Ward, S. Vega, M. Heffernan, A.A. Argun, “Highly Specific Detection of Oxytocin in Saliva” Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24(5), 4832.
- M. Rana, K. Haque, DJ Lim, “ Nanoparticle-Enhanced Drug Delivery Systems for Targeted Cancer Therapy” Biosensors and Nanotheranostics (2025), 2 (1) 1-9
- M. Rana, T. Yilmaz, S. Cohen, S. Beyhan, A.A. Argun, “A novel biosensor for ultrasensitive detection of fungal genes” Biosensors and Bioelectronics (2023), 222, 114986.
- A.A. Argun, M. Rana, “Point-of-care (POC) Assay to Detect Dengue Exposure” Biosensors and Nanotheranostics 2022, 1 (1), 001-006.
- N. Kumar*, M. Rana*, M. Geiwitz, N. I. Khan, M. Catalano, J. C. Ortiz-Marquez, H. Kitadai, A Weber, B. Dweik, X. Ling, T.V. Opijen, A.A. Argun, K. S. Burch. “Rapid, multianalyte detection of opioid metabolites in wastewater” (*co-first authors), ACS Nano (2022), 16 (3), 3704-3714 (highlighted in Science Daily, Boston College, and more)
- N. Kumar, M. Gray, J. C. Ortiz-Marquez, A Weber, C.R. Desmond, A. Argun, T.V. Opijen, K. S. Burch. “Detection of a multi-disease biomarker in saliva with graphene field transistors”. Med. Devices Sens. 2020; 3: e10121.
Conference Abstracts
- M. Rana, S.M. Asil, C. Boutin, M.J. Kachwala, J. Espejo, A.A. Argun (PI) “Detection of EGFR mutations T790M and L858R for therapeutic guidance of NSCLC” 2024 World Conference on Lung Cancer (Abstract # 2024-RA-2397-WCLC), September 7-10, 2024, San Diego, CA, USA.
- Shima M Asil, PhD, Chia-Yi (Jobert) Hsiao, MS, Pengfei Xie, PhD, Avni A Argun, PhD, Muhit Rana, PhD (PI) “Rapid and Reprogrammable Assay for Multiplexed Gene Detection” 2024 MHSRS (Abstract # MHSRS-24-13209), August 26-30, 2024, Kissimmee, FL, USA.
- A Argun, M Rana, A Weber, M Manoukian, A Koh, E Toprak “Electrochemical Sensors to Monitor Multi-Drug Resistant Organisms in the Gut Microbiome” 2019, Electrochemical Society Meeting Abstracts 235, 2094-2094, May 26-30, 2019, Dallas, TX, USA.
- M Rana, A Weber, M Manoukian, B Dweik, A Argun “Highly Specific Detection of Oxytocin in Saliva” 2019, Electrochemical Society Meeting Abstracts 235, 1852-1852, May 26-30, 2019, Dallas, TX, USA.
- A Argun, A Weber, M Manoukian, M Rana, R Pierce, V Lovko, M Henry “Rapid and Low-Cost Field Detection of Marine Toxins” 2019, Electrochemical Society Meeting Abstracts 235, 2000-2000, May 26-30, 2019, Dallas, TX, USA.
- N. Kumar, A Weber, M. Gray, J. C. Ortiz-Marquez, C.R. Desmond, A. Argun, T.V. Opijen, K. S. Burch. “Reproducible fabrication of graphene field effect transistors for detection of CA1”. APS March Meeting 2019, Abstract: E12.00012; Volume 64, Number 2; March 4–8, 2019; Boston, MA, USA.
Patent Applications
- M. Rana, AA Argun, “Rapid and Reprogrammable Assay for Multiplexed Detection of Drug Metabolism Genes” U.S. Patent App. 63/687,437 (Aug 27, 2024)
- AA Argun, M Rana, “Detection of Oxytocin in a Biological Sample” U.S. Patent App. 18/590,417 (Feb 28, 2024)
- AA Argun, M Rana, “Method and system for detecting fungal genes and kit for use with same” US Patent App. 18/295,613 (Nov 23, 2023)
- AA Argun, M Rana, BM Dweik, NI Khan, A Weber, “Method and system for detecting one or more drugs and/or drug metabolites in wastewater” US Patent App. 17/887,347 (Feb 16, 2023)