Overview of Static Vapor Feed Electrolysis
The SVFE is a proton-exchange membrane electrolysis cell stack that electrolyzes water to produce low-humidity, high-purity gaseous hydrogen and oxygen. Unlike conventional electrolyzers, the SVFE does not circulate liquid water to the anode or cathode. This technology utilizes Giner’s novel Water Management Membrane (WaMM™) that allows for dead-ended water feed operation and a bipolar stack configuration. The WaMM™ is an electrically conductive film that facilitates transport of water by means of a concentration gradient into the hydrogen compartment of an electrolyzer.
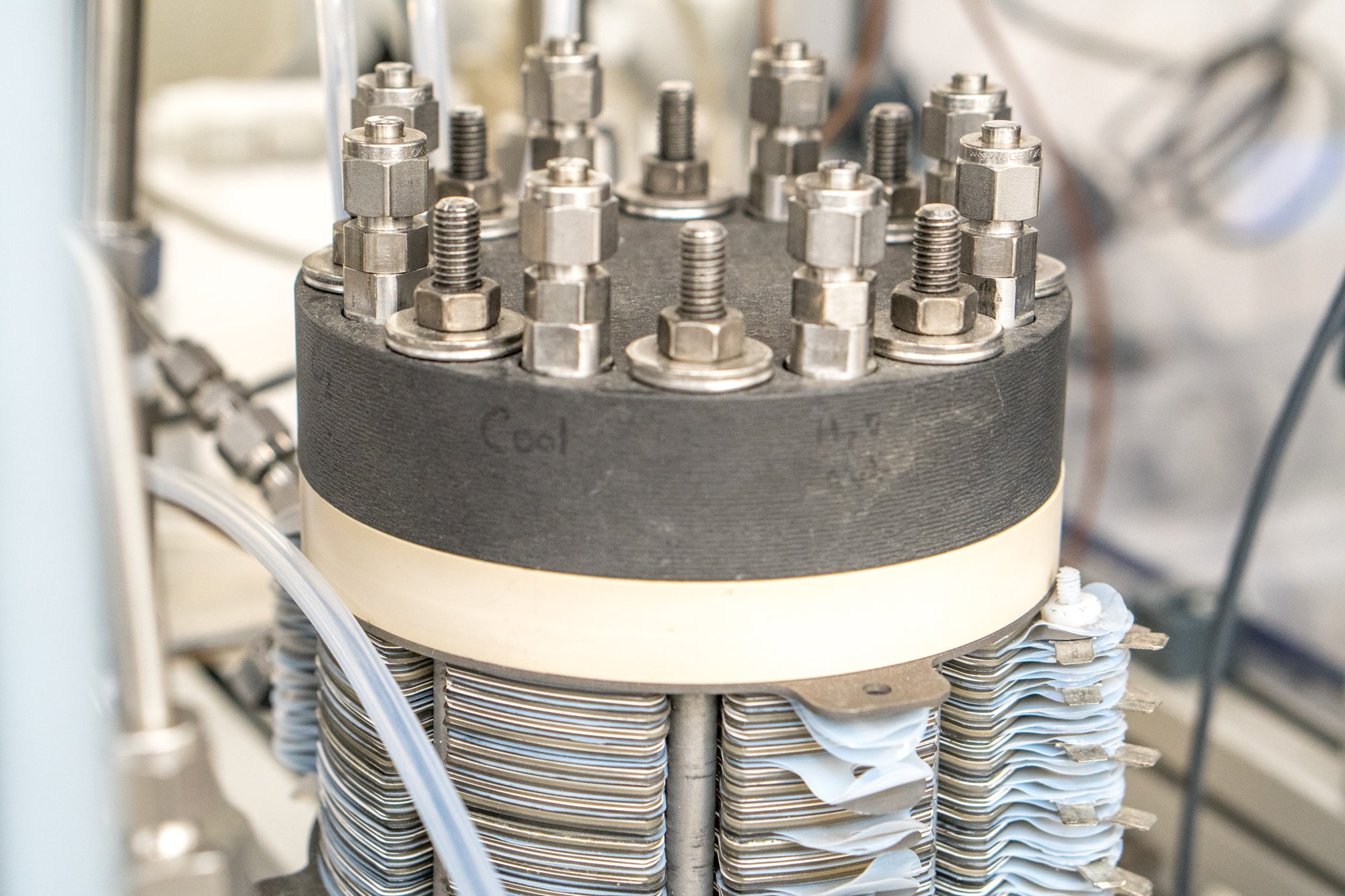
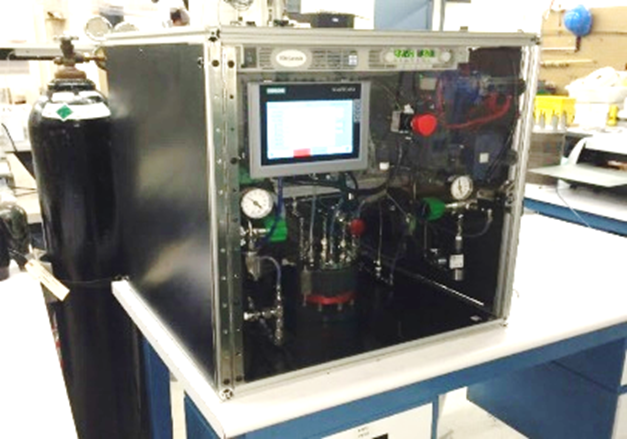


Giner's Static Vapor Feed Electrolyzers
Because no liquid water flows into the anode or cathode, phase separators are not required on the oxygen or hydrogen outlets. Additionally, no water delivery pump is required resulting in increased simplicity and reliability of the supporting balance of plant. This makes the SVFE ideal for aerospace and other applications where a reliable, compact oxygen production system is required. This technology also boasts impressive durability. A single test article has accumulated over 43,000 hours of operation under continuous day/night cycling.
Giner's Current Programs
Static Vapor Feed Electrolysis Cell Stack Redesign and Endurance Testing
Static Vapor Feed Electrolyzer for Life Support Oxygen
Water Management Membrane for Fuel Cells and Electrolyzers